For example:. A scheduling policy is a set of rules that defines the logic by which virtual machines are distributed amongst hosts in the cluster that scheduling policy is applied to.
What's New
Scheduling policies determine this logic via a combination of filters, weightings, and a load balancing policy. The filter modules apply hard enforcement and filter out hosts that do not meet the conditions specified by that filter.
The weights modules apply soft enforcement, and are used to control the relative priority of factors considered when determining the hosts in a cluster on which a virtual machine can run. You can also define new scheduling policies that provide fine-grained control over the distribution of virtual machines. Regardless of the scheduling policy, a virtual machine will not start on a host with an overloaded CPU. See Section 8.
The cluster is considered unbalanced if any host is running more virtual machines than the HighVmCount and there is at least one host with a virtual machine count that falls outside of the MigrationThreshold. Hosts with a CPU load below the low utilization value for longer than the defined time interval will migrate all virtual machines to other hosts so that it can be powered down.
Additional virtual machines attached to a host will not start if that host has reached the defined high utilization value. Set the None policy to have no load or power sharing between hosts for running virtual machines. This is the default mode. When a virtual machine is started, the memory and CPU processing load is spread evenly across all hosts in the cluster.
If host failure occurs, highly available virtual machines will restart properly and any virtual machine can migrate. You can create new scheduling policies to control the logic by which virtual machines are distributed amongst a given cluster in your Red Hat Virtualization environment. The name of the scheduling policy. This is the name used to refer to the scheduling policy in the Red Hat Virtualization Manager.
A set of filters for controlling the hosts on which a virtual machine in a cluster can run. Enabling a filter will filter out hosts that do not meet the conditions specified by that filter, as outlined below:. A set of weightings for controlling the relative priority of factors considered when determining the hosts in a cluster on which a virtual machine can run. This drop-down menu allows you to select a load balancing module to apply. Load balancing modules determine the logic used to migrate virtual machines from hosts experiencing high usage to hosts experiencing lower usage.
This drop-down menu allows you to add or remove properties for load balancing modules, and is only available when you have selected a load balancing module for the scheduling policy. No properties are defined by default, and the properties that are available are specific to the load balancing module that is selected. Instance types can be used to define the hardware configuration of a virtual machine.
Selecting an instance type when creating or editing a virtual machine will automatically fill in the hardware configuration fields. This allows users to create multiple virtual machines with the same hardware configuration without having to manually fill in every field. A set of predefined instance types are available by default, as outlined in the following table:. Administrators can also create, edit, and remove instance types from the Instance Types tab of the Configure window. Fields in the New Virtual Machine and Edit Virtual Machine windows that are bound to an instance type have a chain link image next to them.
If the value of one of these fields is changed, the virtual machine will be detached from the instance type, changing to Custom , and the chain will appear broken. However, if the value is changed back, the chain will relink and the instance type will move back to the selected one. Administrators can create new instance types, which can then be selected by users when creating or editing virtual machines. The new instance type will appear in the Instance Types tab in the Configure window, and can be selected from the Instance Type drop-down list when creating or editing a virtual machine.
Administrators can edit existing instance types from the Configure window.
Improvements
The configuration of the instance type is updated. When a new virtual machine based on this instance type is created, or when an existing virtual machine based on this instance type is updated, the new configuration is applied. Existing virtual machines based on this instance type will display fields, marked with a chain icon, that will be updated.
If the existing virtual machines were running when the instance type was changed, the orange Pending Changes icon will appear beside them and the fields with the chain icon will be updated at the next restart. The instance type is removed from the Instance Types list and can no longer be used when creating a new virtual machine.
Any virtual machines that were attached to the removed instance type will now be attached to Custom no instance type. A MAC address pool is specified for each cluster. The same MAC address pool can be shared by multiple clusters, but each cluster has a single MAC address pool assigned. For more information about assigning MAC address pools to clusters see Section 8. If more than one Red Hat Virtualization cluster shares a network, do not rely solely on the default MAC address pool because the virtual machines of each cluster will try to use the same range of MAC addresses, leading to conflicts.
If there are no further addresses left in the range, the search starts again from the beginning of the range. If one MAC address pool has duplicates disabled, and another has duplicates enabled, each MAC address can be used once in the pool with duplicates disabled but can be used multiple times in the pool with duplicates enabled. You can edit MAC address pools to change the details, including the range of MAC addresses available in the pool and whether duplicates are allowed. After a MAC address pool has been created, you can edit its user permissions.
The user permissions control which data centers can use the MAC address pool. See Section 1. You can remove a created MAC address pool if the pool is not associated with a cluster, but the default MAC address pool cannot be removed.
next-patchlevel - TYPO3 Core - TYPO3 Forge
This summary can alert you to a problem and allows you to analyze the problem area. The information in the dashboard is updated every 15 minutes by default from Data Warehouse, and every 15 seconds by default by the Manager API, or whenever the Dashboard is refreshed. The Dashboard is refreshed when the user changes back from another page or when manually refreshed.
The Dashboard does not automatically refresh. The inventory card information is supplied by the Manager API and the utilization information is supplied by Data Warehouse. The Dashboard is implemented as a UI plugin component, which is automatically installed and upgraded alongside the Manager.
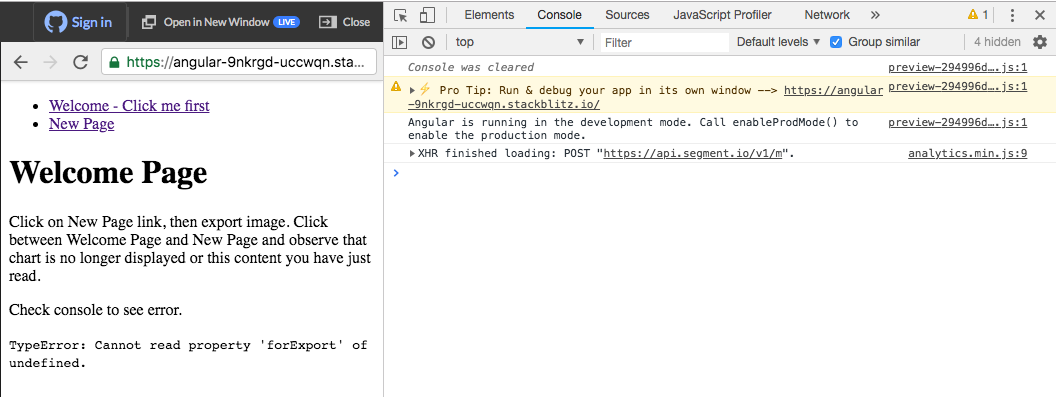
Export limits
The Dashboard requires that Data Warehouse is installed and configured. The top section of the Dashboard provides a global inventory of the Red Hat Virtualization resources and includes items for data centers, clusters, hosts, storage domains, virtual machines, and events. Icons show the status of each resource and numbers show the quantity of the each resource with that status.
The title shows the number of a type of resource and their status is displayed below the title. Clicking on the resource title navigates to the related page in the Red Hat Virtualization Manager. Shows the number of a resource with a warning status. Clicking on the icon navigates to the appropriate page with the search limited to that resource with a warning status.
The search is limited differently for each resource:.
- Analytics Event Tracker.
- dau tu vao forex?
- forex plugin wordpress.
- OSGi Compendium Release 7.
- Applicable to 2.30 version.
Shows the number of a resource with an up status. Clicking on the icon navigates to the appropriate page with the search limited to resources that are up. Shows the number of a resource with a down status. Clicking on the icon navigates to the appropriate page with the search limited to resources with a down status. Shows the number of events with an alert status. Clicking on the icon navigates to Events with the search limited to events with the severity of alert. Shows the number of events with an error status.
Unreal Engine 4.25 Release Notes
Clicking on the icon navigates to Events with the search limited to events with the severity of error. Clicking the donut in the global utilization section of the Dashboard will display a list of the top utilized resources for the CPU, memory or storage. For CPU and memory the pop-up shows a list of the ten hosts and virtual machines with the highest usage. For storage the pop-up shows a list of the top ten utilized storage domains and virtual machines.
The arrow to the right of the usage bar shows the trend of usage for that resource in the last minute. The heatmap of the CPU utilization for a specific cluster that shows the average utilization of the CPU for the last 24 hours. Hovering over the heatmap displays the cluster name. This is calculated by using the average host CPU utilization for each host over the last 24 hours to find the total average usage of the CPU by the cluster.
The heatmap of the memory utilization for a specific cluster that shows the average utilization of the memory for the last 24 hours. The formula used to calculate the memory usage by the cluster is the total utilization of the memory in the cluster in GB. This is calculated by using the average host memory utilization for each host over the last 24 hours to find the total average usage of memory by the cluster. The Storage Utilization section shows the storage utilization in a heatmap.
The heatmap shows the average utilization of the storage for the last 24 hours. The formula used to calculate the storage usage by the cluster is the total utilization of the storage in the cluster. This is calculated by using the average storage utilization for each host over the last 24 hours to find the total average usage of the storage by the cluster. Hovering over the heatmap displays the storage domain name.